Hyundai Motor India adds 11 additional Hyundai Ultra-Fast Charging Infrastructure EV charging stations to its network.
Hyundai Motor India adds 11 additional Hyundai Hyundai Ultra-Fast Charging Infrastructure EV charging stations to its network, enabling speedy and practical 24/7 charging with cutting-edge technology. With the My-Hyundai app, customers can search, navigate, reserve times in advance, pay, and keep track of their progress. By 2027, 100 stations will be installed, according to future plans.
Table of Contents
Customers can utilize the MyHyundai app to further streamline the charging procedure. Through the app, users can find charging stations, find their location, schedule charging times in advance, pay digitally, and keep an eye on the charging state. By 2024, Hyundai intends to add ten or more new locations to its network of ultra-fast chargers. In addition, Hyundai plans to create 100 charging stations by 2027 as part of a deal with the Tamil Nadu government.
In this paper, we conduct a comprehensive technological review of Hyundai ultra-fast charging stations (HUFCS), focusing on two key power electronic conversion stages: AC/DC and DC/DC. Through a detailed analysis, we compare various converters utilized in UFC infrastructure, considering current trends, technical advancements, control strategies, and converter topologies. Additionally, we explore the potential of solid-state transformers (SSTs) in enabling UFC, highlighting their benefits and existing topologies.

One of the primary challenges confronting EVs is their extended charging duration compared to the rapid refueling of internal combustion engine vehicles (ICEVs). To bridge this gap and accelerate EV adoption, the development of ultra-fast charging infrastructure is imperative. By significantly reducing charging times to minutes rather than hours, UFC holds the potential to revolutionize the EV market, making electric vehicles more attractive to consumers.

2. EV Charging Standards: The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) establishes standards for EV charging, encompassing plugs, sockets, connectors, and vehicle inlets. We delve into the specifics of these standards, crucial for ensuring interoperability and safety in EV charging infrastructure.
3. Advancement of UFC Infrastructure: Here, we highlight the progress in UFC infrastructure, focusing on top-selling ultra-fast charging EVs available in the market. By comparing charging times and rates, we underscore the efficacy of UFC in enhancing EV usability and convenience.
4. Energy Trading of Ultra-Fast Charging EVs in Multi-Energy Systems:
This section explores the potential for energy exchange with EVs to reduce peak demand and enhance grid stability. EVs, acting as flexible loads, offer opportunities for demand response programs and load management strategies within multi-energy systems.
5. Battery Storage Considerations for UFCS: Lithium-ion batteries emerge as the preferred energy storage option for EVs, necessitating efficient battery management systems (BMS) for ultra-fast charging. We delve into the intricacies of battery technology and management for optimal UFC performance.
6. Power Electronics Converters: The architecture of UFC involves two crucial power electronic conversion stages: AC/DC and DC/DC. This section scrutinizes various converter topologies and control strategies, crucial for efficient EV charging.
7. Control of Power Electronic Converters: Here, we discuss the control strategies employed in power electronic converters for EV charging, emphasizing the need for adjusting voltage, improving power factor, and minimizing total harmonic distortion (THD) to enhance charging efficiency.
8. Recommended Solid State Transformer Based Hyundai Ultra-Fast Charging Infrastructure of EV: Solid-state transformers (SSTs) hold promise in facilitating UFC by efficiently converting medium AC voltage to low AC voltage. We explore different SST topologies and their potential for enhancing UFC infrastructure.
Quick DC Charging
Quick DC Charging
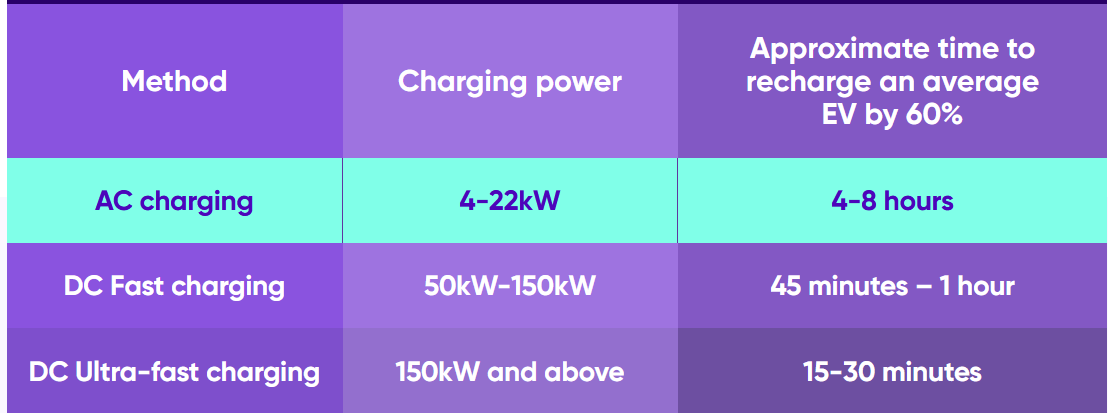
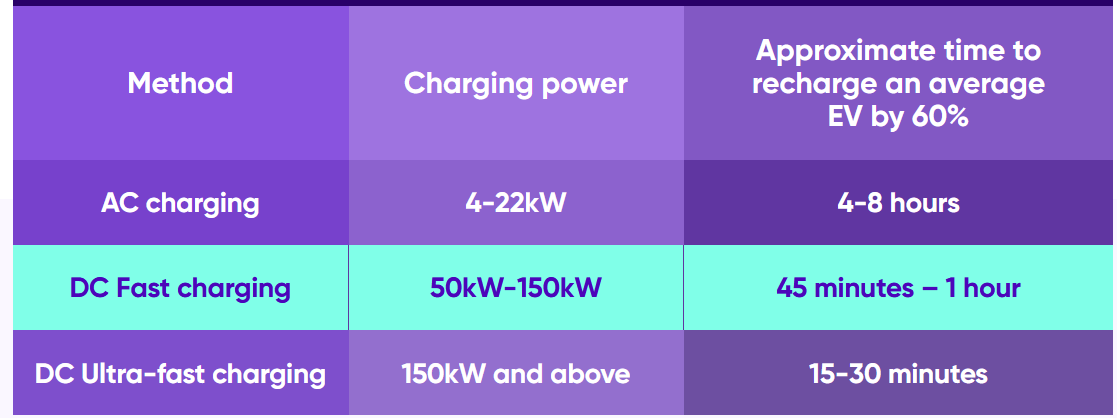
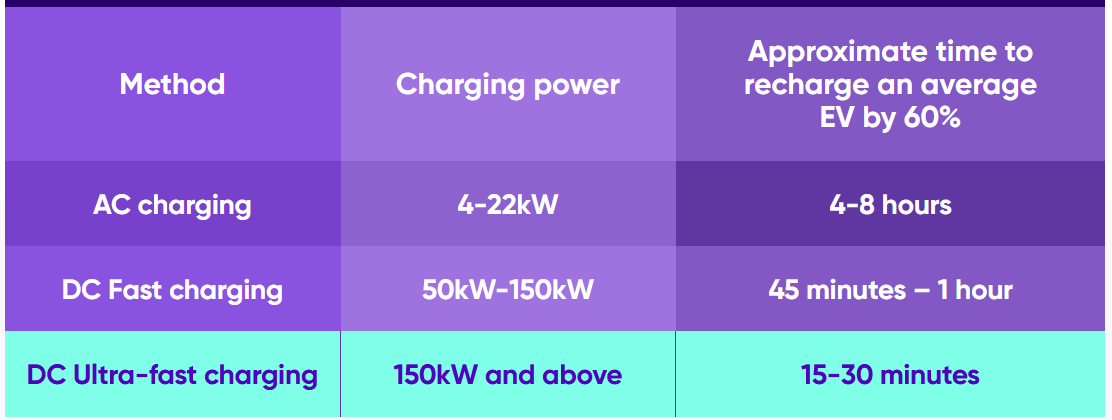
Outside the automobile, DC chargers transform AC power into DC. Fast DC chargers, which have a power output of at least 50kW, are more common in public areas than in private houses. A fast charger would need to run for slightly more than 45 minutes in order to fully recharge an EV from 20% to 80%.
Extremely Quick DC Charging
Extremely Quick DC Charging
These ultra-rapid, or ultra-fast, chargers operate at 150W, which allows them to charge an automobile considerably quicker. Although there aren’t many ultra-fast charging stations in the globe right now, their utilization is growing as a result of them providing a pressing need for customers. The number of ultra-fast charging stations increased by 40% in the first half of 2022 alone in the UK. An ultra-fast charger would require charging for roughly fifteen minutes in order to fully recharge an EV from 20% to 80%.
So, I believe I’ve given you all the information. I hope you enjoyed the post. If you did, don’t forget to like and share it.
Experience the power, feel the comfort, and embrace the evolution for the most recent tech news and reviews, Health tips and many more follow themdakbar Blogs also follow us on Facebook, Twitter, Google News, and Instagram. For access to our most recent videos, subscribe to our YouTube channel.


